Radiant or Convection
Radiant or Convection?
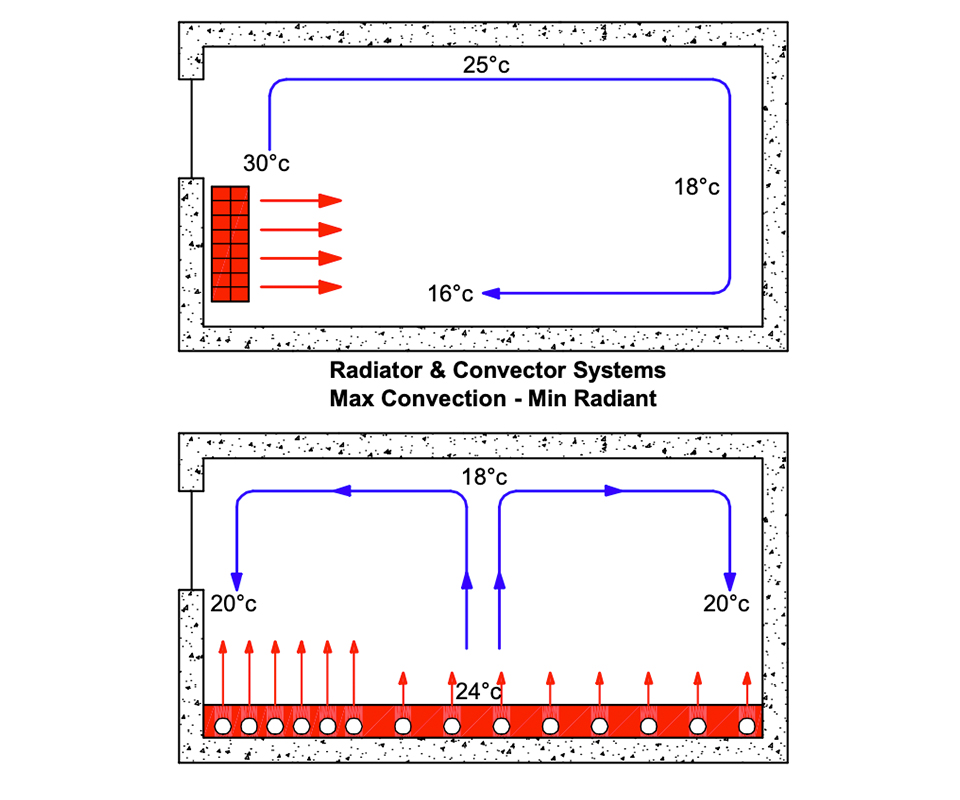
Heating systems which use high temperature emitters such as radiators and convectors need to create a high rate of air convection to work. This generally results in the warmest air being at ceiling or roof level with the coolest at floor level. With today’s better insulated buildings these emitters also tend to be much smaller than in the past and therefore do not evenly distribute the heat to all parts of the area being heated. This often means that comfort conditions within the entire room or area cannot be achieved.
Heating by floor radiant means however reverses this tendency by allowing a much lower surface temperature to be applied to the whole floor which becomes the radiator. This much lower surface temperature does not create convection currents with the result that the floor zone is always warmer than the ceiling or roof zone. Distribution of heat is even across the entire area and there are no cold zones creating an overall feeling of comfort.
This effect is much more apparent in buildings with high ceilings or roofs. With radiant floor heating the temperature from the floor to the ceiling actually reduces as the height increases whilst with convection systems it increases dramatically. This means higher losses through roof and fabric and subsequently higher operating costs.
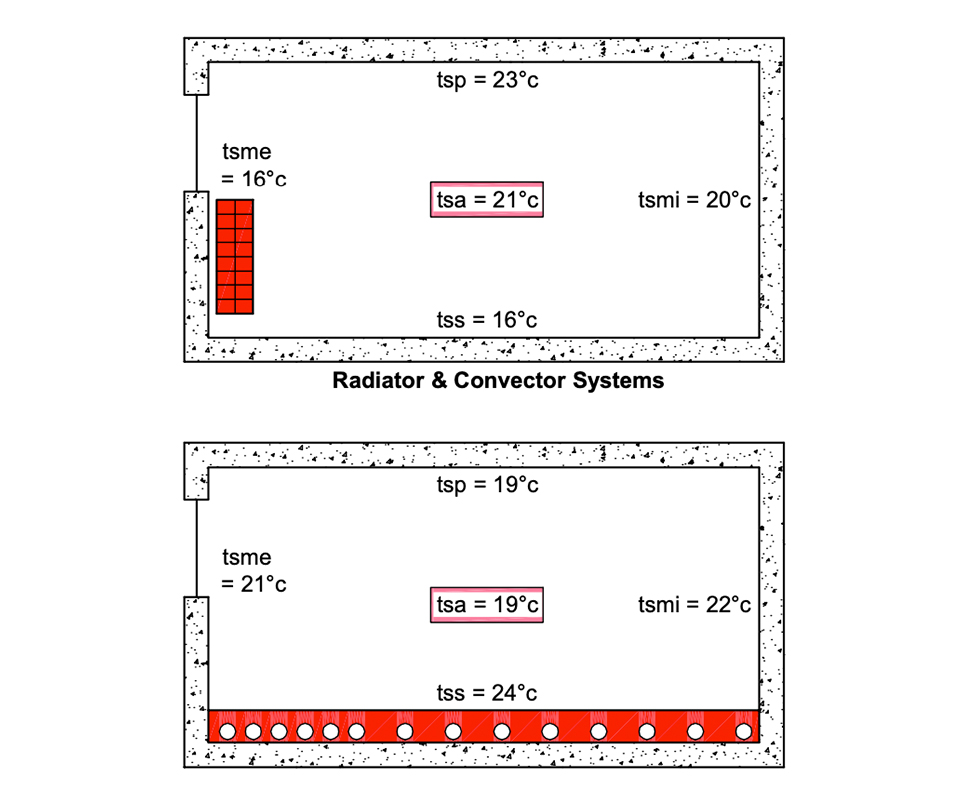
The diagram on the left shows the benefit of radiant floor heating in terms of comfort temperatures. The difference between air and mean radiant temperature in convective systems is much higher than with floor radiant systems. The effect of higher radiant surface temperatures in a room means that a level of comfort will be achieved at a lower air temperature than with convective heating.
The diagram for the convection system indicates lower radiant temperatures and therefore a higher air temperature requirement to achieve comfort conditions.
The diagram for the floor radiant system however results in higher radiant surface temperatures and can therefore achieve comfort conditions at an air temperature of 2°C lower.
This allows the design engineer to use a lower temperature difference when calculating heat losses and no allowance need be added for the height of building. This results in lower energy requirements particularly on larger buildings with high ceilings and roofs such as Churches, Atria, Workshops and similar buildings.
A RADIANT FLOOR SOLUTIONS system when combined with low temperature energy sources such as condensing boilers can provide substantial savings in running cost when compared with other types of heating systems.
Copyright Radiant © 2026. All rights reserved
